Insurance plays a vital role in modern economies by providing financial security and risk management solutions that support economic stability and growth. By mitigating risks and providing a safety net for individuals, businesses, and governments, insurance fosters confidence and encourages investment. Insurance services promote economic development by enhancing resource allocation, supporting innovation, reducing uncertainty, and improving the overall quality of life.
This article explores the multifaceted role of insurance in economic development, including its impact on resource mobilization, investment, entrepreneurship, and poverty alleviation. Additionally, it addresses the role of insurance in managing risks associated with natural disasters, health crises, and technological disruptions.
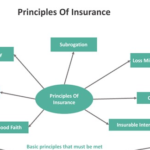
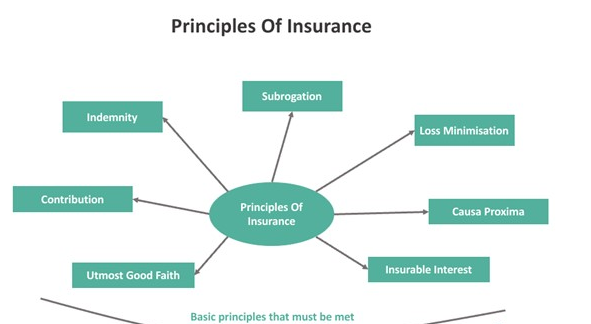
1. Risk Management and Economic Stability
Insurance fundamentally operates as a mechanism for risk management, offering protection against uncertain events such as illness, accidents, property damage, and business interruptions. By pooling risks across many policyholders, insurance companies distribute the financial impact of losses, ensuring that no single individual or business bears the full brunt of an unexpected event.
1.1 Reducing Economic Volatility
Insurance reduces the volatility of economic activities by mitigating the impact of adverse events on individuals and businesses. For example, crop insurance protects farmers from the financial consequences of poor weather conditions or pest infestations, ensuring that agricultural production continues without significant disruptions. Similarly, health insurance helps individuals manage medical expenses, reducing the risk of catastrophic health costs that could lead to personal bankruptcy.
By reducing uncertainty, insurance contributes to economic stability. When individuals and businesses are protected from significant financial losses, they can plan for the future with greater confidence, allowing for smoother consumption and investment patterns. This, in turn, creates a stable economic environment that fosters growth.

1.2 Supporting Risk-Taking and Innovation
Entrepreneurs and businesses are often hesitant to undertake risky ventures due to the fear of failure and financial loss. However, insurance helps alleviate this fear by offering protection against certain risks. For example, liability insurance shields businesses from the financial consequences of lawsuits, and property insurance protects companies from the costs of damage to physical assets.
By managing these risks, insurance encourages innovation and entrepreneurship. Firms are more likely to invest in new technologies, products, and services when they have insurance coverage in place to protect their investments. This entrepreneurial activity drives economic growth by creating new jobs, increasing productivity, and introducing new goods and services to the market.
2. Mobilizing Long-Term Savings and Investment
One of the most critical roles of insurance in economic development is its function as a vehicle for mobilizing long-term savings. Insurance companies collect premiums from policyholders, which are then invested in various financial instruments, including government bonds, corporate securities, and real estate. This capital accumulation plays a crucial role in funding large-scale investments and supporting capital markets.
2.1 Pooling Savings for Productive Use
Through life insurance and pension schemes, insurance companies pool large amounts of capital from individual policyholders. This capital is often invested in long-term projects, such as infrastructure development, which contribute to economic growth. Infrastructure investments, such as roads, bridges, and power plants, are essential for improving productivity and enabling businesses to operate more efficiently.
Furthermore, insurance companies invest in private sector companies, providing the necessary capital for expanding businesses. This capital infusion enables companies to innovate, expand their operations, and create jobs, all of which contribute to economic development.
2.2 Development of Capital Markets
Insurance companies also play a significant role in the development of capital markets by investing in equity and debt markets. As institutional investors, insurance firms provide liquidity and stability to capital markets. Their long-term investment horizon enables them to support the development of large-scale, long-term projects that require stable and sustained financing.
Moreover, insurance companies serve as key stakeholders in the bond markets. By purchasing government bonds and corporate debt, insurance companies provide governments and businesses with the financing needed for economic development projects. For governments, this might include funding infrastructure improvements, healthcare systems, or social welfare programs, while for businesses, it could mean expanding production capacity or entering new markets.
3. Promoting Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development
Entrepreneurship is a crucial driver of economic development, contributing to job creation, innovation, and economic dynamism. Insurance plays a key role in promoting entrepreneurship by providing small businesses and start-ups with the security needed to take risks and grow.
3.1 Providing Protection for Small Businesses
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often face significant challenges in obtaining financing and managing risks, especially in the early stages of development. Insurance offers protection against risks such as property damage, theft, liability, and business interruptions, which can otherwise be devastating to small businesses. For example, if a small manufacturing company experiences a fire in its factory, property insurance ensures that the company can recover and rebuild without facing crippling financial losses.
Business insurance also makes it easier for SMEs to access credit. Lenders are more willing to provide loans to small businesses that have insurance coverage because they are perceived as less risky. This access to credit enables small businesses to invest in expansion, hire more workers, and contribute to overall economic growth.
3.2 Facilitating Innovation and Competition
Insurance fosters competition by enabling smaller firms to enter markets and compete with larger, established companies. By mitigating some of the risks associated with new business ventures, insurance helps level the playing field for smaller firms. This increased competition drives innovation, as companies strive to differentiate themselves and offer superior products and services to consumers.
Additionally, by encouraging innovation through risk management, insurance contributes to technological advancement. Companies are more likely to invest in research and development when they know they are protected from some of the financial risks associated with failed experiments or technological disruptions.
4. Reducing Poverty and Enhancing Social Welfare
Insurance also plays a crucial role in social development by reducing poverty and enhancing social welfare. In many cases, unforeseen events, such as natural disasters, accidents, or health crises, can push individuals and families into poverty. Insurance provides a financial safety net that helps people recover from these events without falling into financial hardship.
4.1 Health Insurance and Poverty Alleviation
Access to health insurance is essential for improving public health and reducing poverty. Medical expenses can be a significant burden for individuals, especially in countries where healthcare costs are high. Health insurance helps alleviate this burden by covering medical expenses, ensuring that individuals have access to necessary healthcare without depleting their savings or going into debt.
By providing access to healthcare, insurance improves the overall health of the population, which is critical for economic development. A healthy workforce is more productive and better able to contribute to economic activities. Additionally, when families are not burdened by excessive healthcare costs, they can allocate more resources to education, housing, and other areas that improve their overall well-being.

4.2 Microinsurance for Low-Income Populations
Microinsurance is a form of insurance designed to cater to low-income populations who are typically underserved by traditional insurance products. In developing countries, microinsurance programs provide protection against risks such as illness, natural disasters, and crop failure, helping vulnerable populations manage the financial impact of these events.
By offering affordable insurance products to low-income individuals, microinsurance plays a significant role in poverty reduction. It enables households to recover from financial shocks and avoid falling into poverty, while also encouraging savings and investment. For example, in rural areas where agriculture is the primary source of income, crop insurance helps farmers recover from poor harvests, ensuring that they can continue farming and supporting their families.
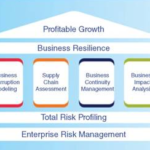
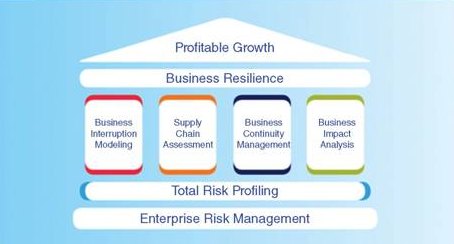
5. Managing Risks Associated with Natural Disasters
Natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, can have devastating effects on economies, particularly in regions that are prone to these events. Insurance is critical for managing the financial risks associated with natural disasters, enabling economies to recover more quickly and reducing the long-term economic impact.
5.1 Disaster Insurance and Economic Resilience
Disaster insurance provides financial protection against the costs of rebuilding and recovery after natural disasters. For businesses, this means that they can restore operations more quickly, minimizing disruptions to economic activities. For governments, insurance reduces the fiscal burden of disaster recovery, allowing public funds to be allocated more efficiently.
By promoting faster recovery and reducing the long-term economic damage caused by natural disasters, insurance enhances economic resilience. This is particularly important for developing countries, where the economic impact of natural disasters can be severe and long-lasting.
5.2 Climate Risk Insurance
As climate change increases the frequency and severity of natural disasters, climate risk insurance is becoming an essential tool for managing these risks. Climate risk insurance programs, often developed in partnership with governments and international organizations, provide protection against the financial losses caused by climate-related events. These programs are particularly important for vulnerable populations, such as small-scale farmers, who are at greater risk of losing their livelihoods due to changing weather patterns.
6. Insurance and Technological Advancements
Technology is transforming the insurance industry, with innovations such as big data, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain changing how insurance products are designed, priced, and delivered. These advancements not only improve the efficiency of insurance companies but also enhance their ability to support economic development.
6.1 Improved Risk Assessment and Pricing
Big data and AI allow insurance companies to collect and analyze vast amounts of data, improving their ability to assess risks and price insurance products accurately. For example, telematics devices in cars provide real-time data on driving behavior, enabling insurers to offer personalized auto insurance premiums based on individual risk profiles. This improves the affordability of insurance and makes it more accessible to a broader population.
6.2 Expanding Insurance Coverage
Technological advancements are also expanding access to insurance in underserved markets. Digital platforms and mobile technology enable insurance companies to reach remote and rural populations that were previously excluded from traditional insurance markets. For example, mobile-based microinsurance products allow low-income individuals to purchase insurance coverage using their phones, making insurance more accessible and affordable.
Conclusion
The role of insurance in economic development cannot be overstated. By providing financial protection, mobilizing long-term savings, supporting entrepreneurship, reducing poverty, and managing risks associated with natural disasters and technological disruptions, insurance is a critical driver of economic stability and growth. As economies continue to evolve and face new challenges, the insurance industry will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of global development.