Risk management is a fundamental aspect of both personal and business financial planning. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could lead to financial loss or damage. Insurance is one of the most important tools in risk management, providing financial protection against unexpected events such as accidents, natural disasters, illness, and death. By transferring the financial risk from the individual or business to an insurance provider, insurance policies help individuals, families, and organizations manage their exposure to risks and safeguard their assets.
This article will explore the concept of risk management, the various types of insurance available, and how these forms of insurance address different types of risks.
1. The Concept of Risk Management
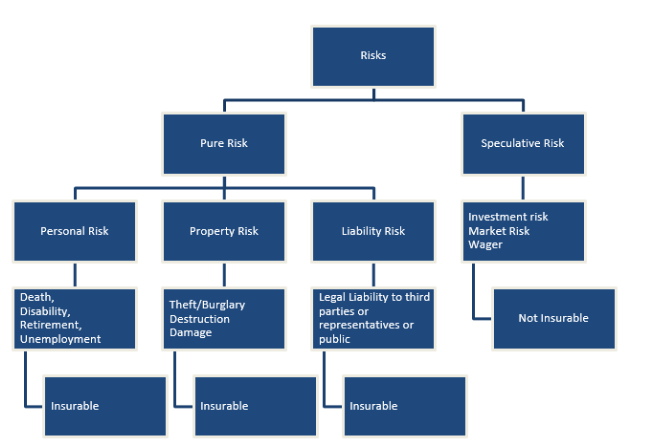
Risk management is a process used to evaluate potential risks and develop strategies to minimize or eliminate their impact. Risks are present in virtually every aspect of life, whether it’s personal health, property ownership, or operating a business. In the context of insurance, risk management involves understanding the likelihood of an event occurring (such as an accident or illness) and the potential financial consequences if it does occur.
The risk management process typically follows these steps:
- Risk Identification: The first step involves identifying potential risks that could lead to financial loss. This could include natural disasters, theft, medical emergencies, or even legal liabilities.
- Risk Assessment: After identifying risks, the next step is to assess the likelihood of these risks occurring and the potential financial impact. This helps determine which risks need to be prioritized.
- Risk Control: This step involves taking actions to reduce or mitigate the risks identified. For example, installing fire alarms or using proper security measures can help reduce the risk of property damage.
- Risk Transfer: Risk transfer refers to the use of insurance as a tool to shift the financial burden of a potential risk to an insurance company. By purchasing an insurance policy, individuals or businesses can transfer the cost of a potential loss to the insurer.
- Risk Monitoring and Review: The final step is to regularly review and monitor the effectiveness of the risk management strategies. As circumstances change, such as a new health condition or the purchase of additional assets, insurance coverage may need to be adjusted.
Insurance plays a key role in risk transfer, allowing people and businesses to protect themselves from significant financial loss in exchange for regular premium payments. Different types of insurance address different categories of risks, providing tailored coverage for a range of possible scenarios.
2. Types of Insurance in Risk Management
Insurance is categorized into various types based on the specific risks it covers. Each type of insurance is designed to address particular needs, helping to mitigate the financial consequences of unexpected events. Here, we will explore the main types of insurance that form the backbone of risk management.
2.1 Life Insurance
Life insurance is one of the most essential types of insurance for personal financial risk management. It provides financial support to beneficiaries (such as family members) in the event of the policyholder’s death. Life insurance is especially important for individuals who have dependents, such as children or spouses, who would suffer financially from the loss of the primary breadwinner.

There are several types of life insurance policies, each with its own risk management benefits:
- Term Life Insurance: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period (e.g., 10, 20, or 30 years). If the policyholder dies during the term, the beneficiaries receive a death benefit. Term insurance is often more affordable but does not accumulate cash value.
- Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance provides coverage for the policyholder’s entire life and includes a savings component (cash value) that grows over time. It is more expensive than term insurance but offers lifelong protection.
- Universal Life Insurance: Universal life insurance is similar to whole life insurance but offers more flexibility in terms of premium payments and death benefits. Policyholders can adjust the policy to meet their changing needs over time.
Life insurance helps manage the risk of financial instability caused by the untimely death of a family member by providing funds for funeral expenses, debts, and ongoing living expenses for dependents.
2.2 Health Insurance
Health insurance is crucial in managing the financial risk associated with medical expenses. Healthcare costs can be overwhelming, particularly in cases of severe illness, accidents, or chronic conditions. Health insurance provides coverage for medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, medications, surgeries, and preventive care.
There are several types of health insurance plans:
- Individual Health Insurance: These plans are purchased by individuals or families and provide coverage for a wide range of medical services. They are typically purchased through private insurers or government marketplaces.
- Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance: Many companies provide health insurance to their employees as part of a benefits package. In these plans, the employer typically covers a portion of the premium, making it more affordable for employees.
- Government-Sponsored Health Insurance: Government programs like Medicare and Medicaid provide health insurance to specific groups, such as the elderly, disabled, or low-income individuals. These programs are essential in ensuring access to healthcare for vulnerable populations.
Health insurance mitigates the financial risk of medical emergencies and long-term care, making it a key component of risk management for individuals and families.
2.3 Auto Insurance
Auto insurance is mandatory in most countries, including the United States, and protects individuals from financial loss related to automobile accidents or damage. Auto insurance covers a range of risks, including damage to the vehicle, liability for injury to others, and legal fees in the event of a lawsuit.
Auto insurance policies typically include several types of coverage:
- Liability Coverage: This covers damages to other people’s property and medical expenses for injuries if the policyholder is at fault in an accident.
- Collision Coverage: This covers the cost of repairing or replacing the policyholder’s vehicle if it is damaged in an accident.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This covers damage to the policyholder’s vehicle from non-collision events, such as theft, fire, or natural disasters.
Auto insurance plays a critical role in risk management by protecting individuals from the potentially high costs associated with car accidents, property damage, or injuries.
2.4 Homeowners and Renters Insurance
Homeowners insurance protects individuals from the financial risks associated with owning a home, including damage from fire, theft, or natural disasters. This type of insurance typically covers both the structure of the home and the homeowner’s personal belongings.
For those who rent rather than own a home, renters insurance provides similar coverage for personal property and liability, but does not cover the building itself.
Homeowners and renters insurance policies generally include the following coverage:
- Property Coverage: This covers damage to the physical structure of the home (for homeowners) and personal belongings (for both homeowners and renters) from covered perils such as fire, theft, or vandalism.
- Liability Coverage: This covers legal fees and damages if someone is injured on the property and the homeowner or renter is found to be liable.
Homeowners and renters insurance is a critical component of risk management for property owners and renters, providing protection against both property damage and liability risks.
2.5 Disability Insurance
Disability insurance is designed to provide income replacement if an individual becomes unable to work due to a disability or illness. This type of insurance is particularly important for individuals who rely on their income to support themselves and their families.
There are two primary types of disability insurance:
- Short-Term Disability Insurance: This provides income replacement for a limited period, usually up to six months, for temporary disabilities.
- Long-Term Disability Insurance: This provides income replacement for an extended period, often until the individual can return to work or reach retirement age.
Disability insurance helps manage the financial risk associated with the loss of income due to illness or injury, ensuring that individuals can continue to meet their financial obligations even if they are unable to work.
2.6 Liability Insurance
Liability insurance protects individuals and businesses from the financial consequences of legal liabilities, such as lawsuits for bodily injury, property damage, or negligence. It is particularly important for businesses, professionals, and individuals who could be at risk of being sued for damages.
Some common types of liability insurance include:
- General Liability Insurance: This provides coverage for businesses and protects them from claims of bodily injury or property damage resulting from business operations.
- Professional Liability Insurance: Also known as errors and omissions (E&O) insurance, this protects professionals (such as doctors, lawyers, and accountants) from claims of negligence or malpractice.
- Personal Liability Insurance: This provides coverage for individuals if they are sued for causing injury to another person or damage to their property.
Liability insurance is essential in risk management, particularly for businesses and professionals, as it helps protect against potentially crippling legal expenses and damages.
2.7 Business Insurance
Businesses face a wide range of risks, from property damage to employee injuries to cyberattacks. Business insurance is designed to protect companies from these financial risks, ensuring their continued operation in the face of unexpected events.
Some key types of business insurance include:
- Property Insurance: This covers damage to the physical assets of a business, such as buildings, equipment, and inventory.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: This provides coverage for employees who are injured or become ill as a result of their job.
- Cyber Liability Insurance: As businesses increasingly rely on technology, cyber liability insurance protects companies from financial losses resulting from data breaches or cyberattacks.
- Business Interruption Insurance: This provides coverage for lost income if a business is forced to temporarily close due to a covered event, such as a natural disaster.
Business insurance is a crucial component of risk management for companies, ensuring that they can recover from unexpected events and continue their operations.
3. The Role of Insurance in Risk Management
Insurance is an integral part of risk management, providing a way to transfer the financial burden of potential risks to an insurance provider. By offering financial protection against various types of risks, insurance helps individuals and businesses safeguard their assets, income, and future stability.
However, insurance is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Effective risk management requires selecting the right types and levels of insurance coverage based on individual needs, risk tolerance, and financial circumstances. Regularly reviewing and updating insurance policies as circumstances change is also essential for ensuring adequate protection.
In conclusion, risk management through insurance is a critical strategy for mitigating the financial impact of unexpected events. From life and health insurance to auto and business insurance, different types of coverage address a wide range of risks, providing individuals, families, and businesses with the peace of mind and security they need to thrive.